Edge Computing: Processing Data Closer to the Source
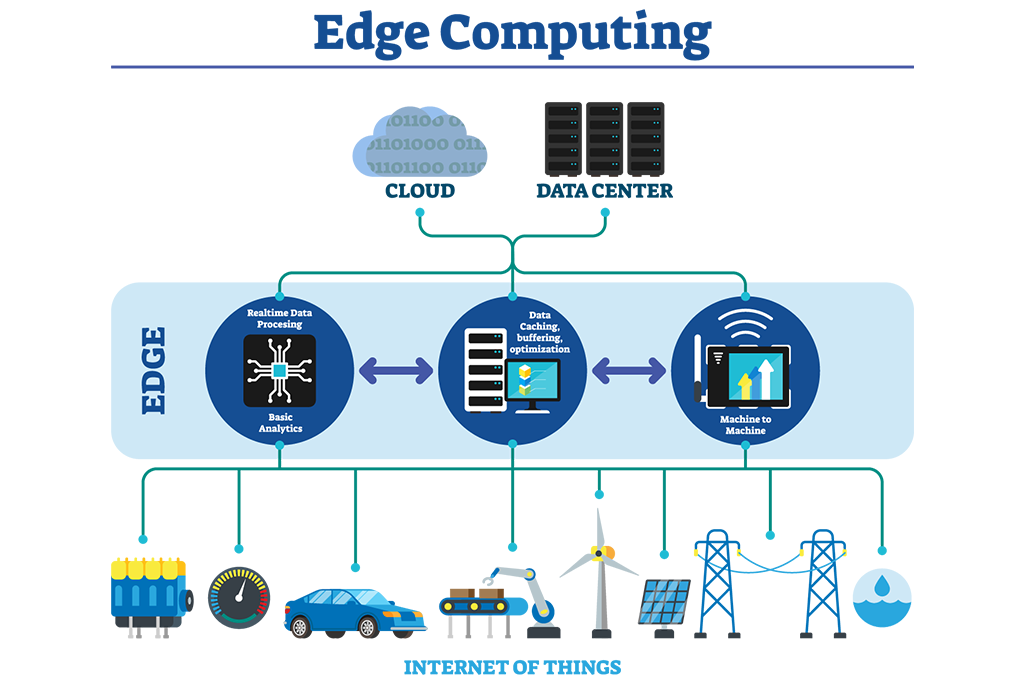
Edge computing represents a fundamental shift in how we process and analyze data, moving computational resources closer to where data is generated rather than relying solely on centralized cloud data centers. This distributed computing paradigm reduces latency, improves performance, and enables real-time decision-making for applications that require immediate responses. As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands and devices generate unprecedented amounts of data, edge computing becomes essential for managing bandwidth limitations, privacy concerns, and the need for instantaneous processing in critical applications. The architecture of edge computing involves deploying computing resources at various points between data sources and centralized cloud infrastructure, creating a continuum of processing capabilities. These edge nodes can range from small embedded processors in IoT devices to more powerful edge servers located in cellular towers, retail stores, or manufacturing facilities. This distributed approach allows data to be processed locally when immediate responses are needed, while still maintaining connections to cloud resources for more complex analytics and long-term storage. Latency reduction represents one of the most significant advantages of edge computing, particularly crucial for applications requiring real-time responses. Autonomous vehicles, for example, cannot afford the delay of sending sensor data to distant cloud servers and waiting for processing results when making split-second safety decisions. By processing critical data locally, edge computing enables reaction times measured in milliseconds rather than seconds. Similarly, industrial automation systems require immediate responses to sensor inputs to maintain safety and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Bandwidth optimization becomes increasingly important as the number of connected devices grows exponentially. Instead of transmitting all raw data to centralized servers, edge computing allows for local processing and filtering, sending only relevant insights or summaries to the cloud. A smart security camera, for instance, can analyze video feeds locally to detect unusual activity and only transmit alerts rather than continuous video streams. This approach significantly reduces network traffic and associated costs while maintaining system effectiveness. Privacy and security benefits emerge from edge computing's ability to process sensitive data locally rather than transmitting it across networks to distant servers. Healthcare devices can analyze patient data at the edge to detect emergencies while keeping personal health information localized. Financial institutions can process transactions locally to reduce exposure to network-based attacks while maintaining compliance with data protection regulations. Smart city applications utilize edge computing for traffic management, where sensors and cameras at intersections process traffic patterns locally to optimize signal timing and manage flow in real-time. Emergency response systems benefit from edge computing's ability to continue functioning even when network connections to centralized systems are disrupted. During natural disasters or infrastructure failures, edge devices can maintain critical operations and local decision-making capabilities. Retail environments leverage edge computing for personalized customer experiences, inventory management, and loss prevention. Smart shelves can monitor product levels and automatically reorder items, while facial recognition systems can identify VIP customers and provide personalized service recommendations. Manufacturing industries implement edge computing for predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization. Sensors throughout production lines can detect anomalies immediately and adjust processes without waiting for cloud-based analysis. Challenges in edge computing include device management, security across distributed systems, and ensuring consistent performance across varied hardware platforms.